FIFA has 208 member associations, three more than the International Olympic Committee and five fewer than the International Association of Athletics Federations.
The need for a single body to oversee the game became apparent at the beginning of the 20th century with the increasing popularity of international fixtures. FIFA was founded in Paris on 21 May 1904; the French name and acronym remain, even outside French-speaking countries. The founding members were Belgium, Denmark, France, The Netherlands, Spain, Sweden and Switzerland. Also, that same day, the German Association declared its intention of affiliating through a telegram. Its first president was Robert Guérin.
Guérin was replaced in 1906 by Daniel Burley Woolfall from England, by now a member association. The next tournament staged, the football competition for the 1908 Olympics in London was more successful, despite the presence of professional footballers, contrary to the founding principles of FIFA.
Membership of FIFA expanded beyond Europe with the application of South Africa in 1908, Argentina and Chile in 1912, and Canada and the United States in 1913.
During World War I, with many players sent off to war and the possibility of travel for international fixtures severely limited, there were few international fixtures, and the organisation's survival was in doubt. Post-war, following the death of Woolfall, the organisation was run by Dutchman Carl Hirschmann. It was saved from extinction, but at the cost of the withdrawal of the Home Nations (of the United Kingdom), who cited an unwillingness to participate in international competitions with their recent World War enemies. The Home Nations later resumed their membership.
The FIFA collection is held by the National Football Museum in England.
Structure
Main article: List of FIFA Member Associations
FIFA is an association established under the Laws of Switzerland. Its headquarters are in Zürich.FIFA's supreme body is the FIFA Congress, an assembly made up of representatives from each affiliated member association. The Congress assembles in ordinary session once every year and, additionally, extraordinary sessions have been held once a year since 1998. Only the Congress can pass changes to FIFA's statutes.
Congress elects the President of FIFA, its General Secretary and the other members of FIFA's Executive Committee. The President and General Secretary are the main officeholders of FIFA, and are in charge of its daily administration, carried out by the General Secretariat, with its staff of approximately 280 members.
FIFA's Executive Committee, chaired by the President, is the main decision-making body of the organisation in the intervals of Congress. FIFA's worldwide organisational structure also consists of several other bodies, under authority of the Executive Committee or created by Congress as standing committees. Among those bodies are the Finance Committee, the Disciplinary Committee, the Referees Committee, etc.
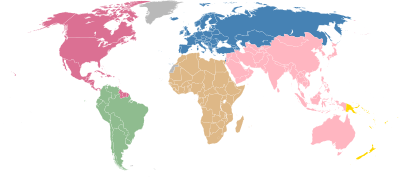
Aside from its worldwide institutions (presidency, Executive Committee, Congress, etc.) there are six confederations recognised by FIFA which oversee the game in the different continents and regions of the world. National associations, and not the continental confederations, are members of FIFA. The continental confederations are provided for in FIFA's statutes. National associations must claim membership to both FIFA and the confederation in which their nation is geographically resident for their teams to qualify for entry to FIFA's competitions (with a few geographic exceptions listed below):
- AFC – Asian Football Confederation in Asia and Australia
- CAF – Confédération Africaine de Football in Africa
- CONCACAF – Confederation of North, Central American and Caribbean Association Football in North America and Central America
- CONMEBOL – Confederación Sudamericana de Fútbol in South America
- OFC – Oceania Football Confederation in Oceania
- UEFA – Union of European Football Associations in Europe.
Guyana and Suriname have always been CONCACAF members despite being South American countries.
In total, FIFA recognises 208 national associations and their associated men's national teams as well as 129 women's national teams; see the list of national football teams and their respective country codes. Curiously, FIFA has more member states than the United Nations, as FIFA recognises several non-sovereign entities as distinct nations, such as the four Home Nations within the United Kingdom or politically disputed territories such as Palestine[2]. The FIFA World Rankings are updated monthly and rank each team based on their performance in international competitions, qualifiers, and friendly matches. There is also a world ranking for women's football, updated four times a year.
No comments:
Post a Comment